A Phylogenetic Tree Has Which of the Following Attributes
All life on Earth is part of a single phylogenetic tree indicating common ancestry. The leopard is more closely related to the tiger than to the snow leopard.

Bland L M Et Al 2015 Predicting The Conservation Status Of Data Deficient Species Conserv Conservation Biology Biodiversity Conservation Conservation
The relative lengths of the frog and mouse branches in the phylogenetic tree in the figure below indicate that.

. Select all that apply. The primary purpose of a phylogenetic tree is to be able to trace evolutionary relationships amongst organisms. In a rooted phylogenetic tree each node with descendants represents the.
The pattern of branching in a phylogenetic tree reflects how species or other groups evolved from a series of common ancestors. D none of the above. The more shared derived characters two organisms share the closer is their evolutionary relationship - that is the more recently their common ancestor lived.
Structure of Phylogenetic Trees. Like every systematic model a phylogenetic tree paradigm has some strengths and limitations which are mentioned below. Based on structural cellular biochemical and genetic characteristics biologists classify life on Earth.
On the phylogenetic tree close relationships are shown by a recent fork from the supporting branch. A phylogenetic tree can be read like a map of evolutionary history. A phylogenetic tree it is a mathematical graphical representation of the history and ancestor-descendant relationships of groups populations species or any other taxonomic category.
Each node is called a taxonomic unit. Scientists call such trees rooted which means there is a single ancestral lineage typically drawn from the bottom or left to which all organisms. Many phylogenetic trees have a single lineage at the base representing a common ancestor.
The homolog has evolved more slowly in mice. Making a phylogenetic tree. Which can be concluded from a comparison of the two phylogenetic trees.
Which domains have exhibited endosymbiosis. The closer the fork in the branch between two organisms the closer is their evolutionary relationship. Make the inference about the most common ancestor of the leaves or branches of the tree.
In trees two species are more related if they have a more recent. Those with low divergence share a lot of DNA in sequence and are more closely related. A phylogenetic tree has which of the following attributes.
Morphological and molecular. Which statements about the phylogenetic tree are true. A possible phylogenetic tree for the three domains of life.
A branches that are closer together have a more recent common ancestor. You can interpret the degree of relationship between two organisms by looking at their positions on a phylogenetic tree. Phylogenetic trees are hypotheses not definitive facts.
Common Ancestor STOP Sample 3 Sample I Sample 2 Sample 4. Types of Phylogenetic Trees. Theoretically all phylogenetic trees can be grouped in the tree of life constituting the universal tree.
A phylogenetic tree is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical or genetic characteristics. The second tree is based on structure genetics and evolutionary history. DNA is particularly helpful.
A paraphyletic group consists of a common ancestor and some of its descendants. A phylogenetic tree is a diagram that represents evolutionary relationships among organisms. Phylogenetic evolutionary Tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities that are believed to have a common ancestor.
Make an illustration about the leaves or branches and do not make any assumption regarding the most common ancestor. A paraphyletic group consists of an ancestral population and all of its descendants. Which of the following statements about phylogenetic trees is true.
The phylogenetic tree does not rank species unlike the Linnean model that artificially ranks organisms into Kingdoms. C a phylogenetic tree is now understood to be meaningless and arbitrary-scientists no longer use them. 2 For each state s s01rof each character cc12 m the set of all u.
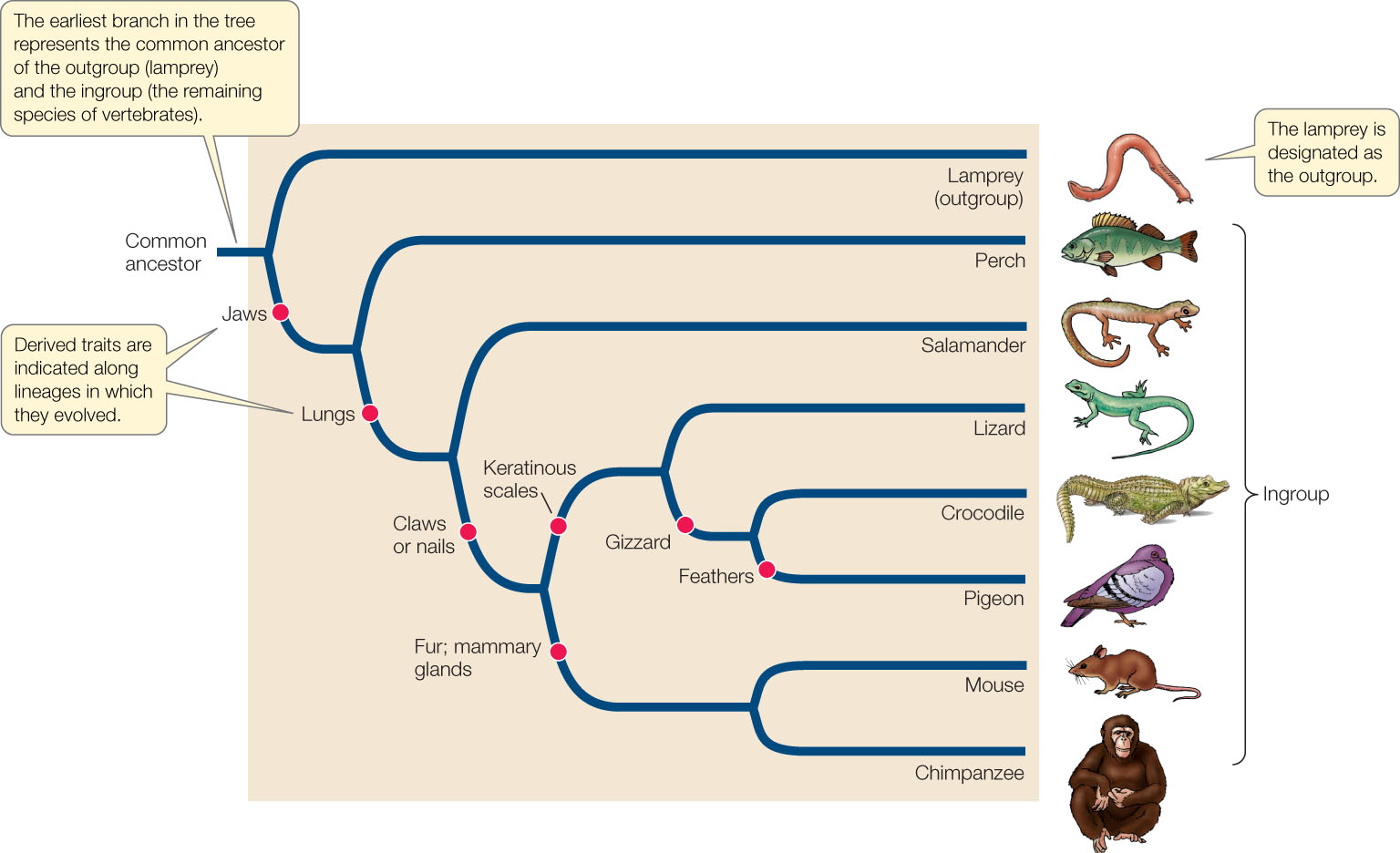
Genetics Morphology Development Biochemistry Fossils etc. The phylogenetic tree shown here displays the major clades of chordates. The primary purpose of a phylogenetic tree is to be able to develop species and genus names of new discovered organisms.
Strengths The model demonstrates the historical origin of any unit individual or species. The first tree is based on physical characteristics. Phylogenetic trees not only show how closely related organisms are but also help map out the evolutionary history or phylogeny of life on Earth.
A perfect phylogenetic tree forMis a rooted tree Twith exactly n leaves that obeys the following properties. Internal nodes are generally called hypothetical taxonomic units In a phylogenetic tree each node with. Phylogenetic trees can have different forms they may be oriented sideways inverted most recent at bottom or the branches may be curved.
Descendants of organism d have legs. Birds and ray-finned fishes have a notochord and. The following question refers to this phylogenetic tree depicting the origins of life and the three domains.
Consider these phylogenetic trees. Connecting lines indicate instances of gene or genome transfer and time is indicated from left to right. A bacterium has the following characteristics It adheres to the.
This tree has a maximum of two descendants arising from each of the interior. The primary purpose of a phylogenetic tree is to be able to determine which. Based on evidence from.
Sequence they have in common so the organisms are not as related. If you were using cladistics to build a phylogenetic tree of cats which of the following would be the best outgroup. B branches that are closer together share broad general similarity.
These graphic representations have revolutionized the. Fill in the phylogenetic tree below with Samples 1 through 4 to summarize the relatedness of the organisms that supplied the samples. 1 Each of the n objects labels exactly one leaf of T.
The process of analyzing this data to understand species diversity and relationships.

Phylogenetic Trees Showing The Evolution Of Projectile Point Taxa From Download Scientific Diagram
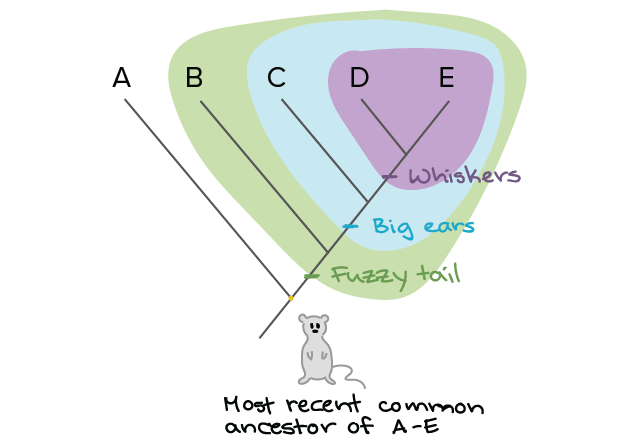
Building A Phylogenetic Tree Article Khan Academy

Como Elaborar Un Genograma Paso A Paso Social Work Practice Step Guide Special Symbols

The Global Flora Open Access The Phylogeny Of Angiosperms Poster A Visual Summary Of Apg Iv Family Relationships And Floral Diversity Ciencias Botanica Bioma
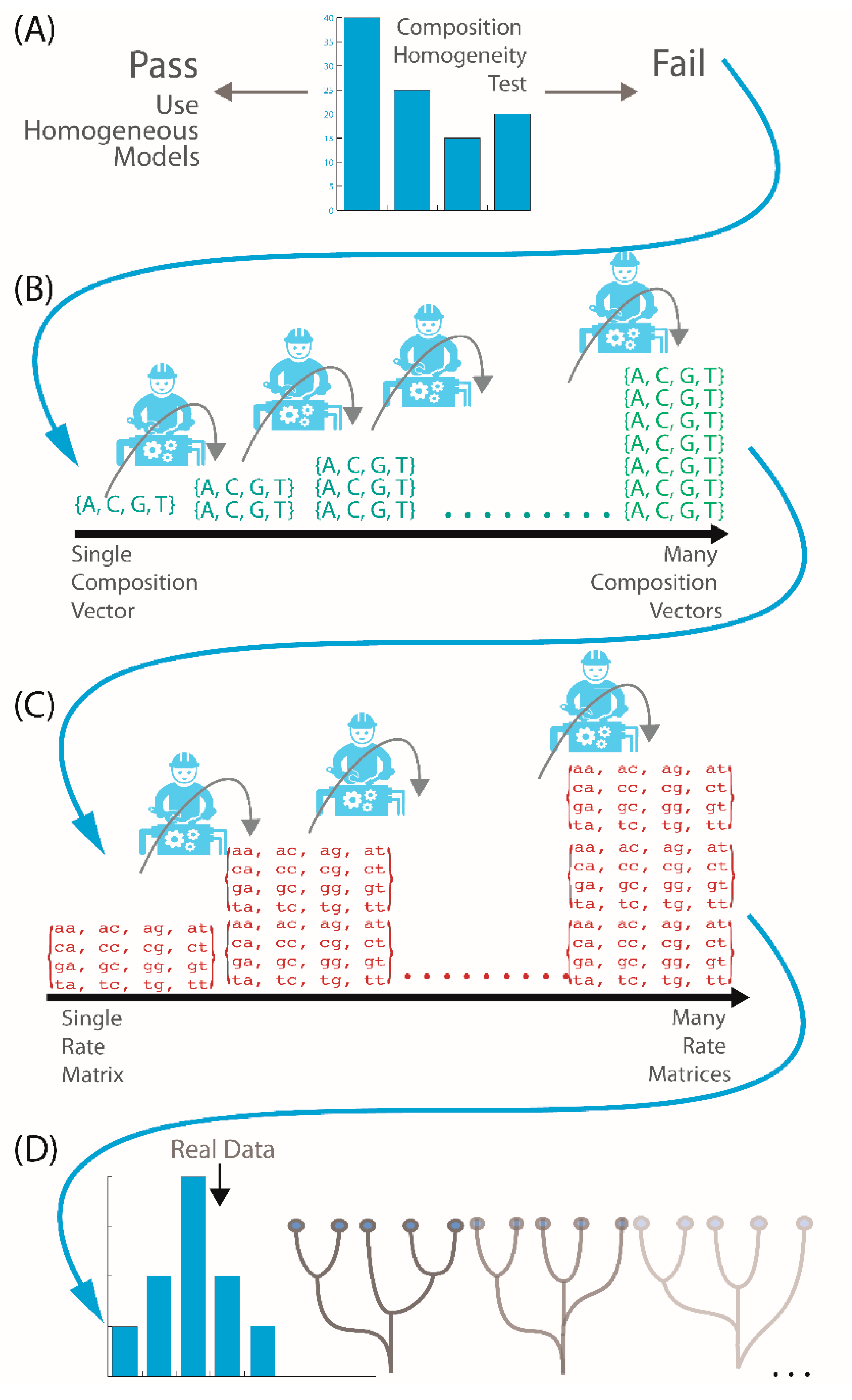
Computation Free Full Text A Guide To Phylogenetic Reconstruction Using Heterogeneous Models A Case Study From The Root Of The Placental Mammal Tree Html

The Secret Rainforest Hidden At The Heart Of An African Volcano In Pictures Rainforest African Picture
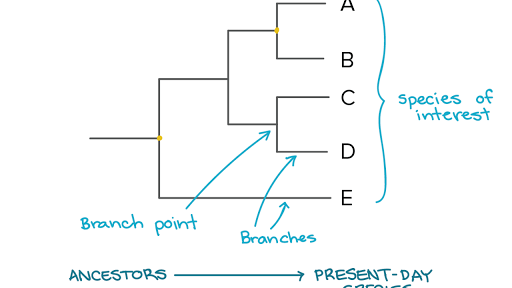
Phylogenetic Trees Evolutionary Tree Article Khan Academy

Marguerite Sauvage Fashion Illustration Fashion Illustration Illustration Fashion Drawing
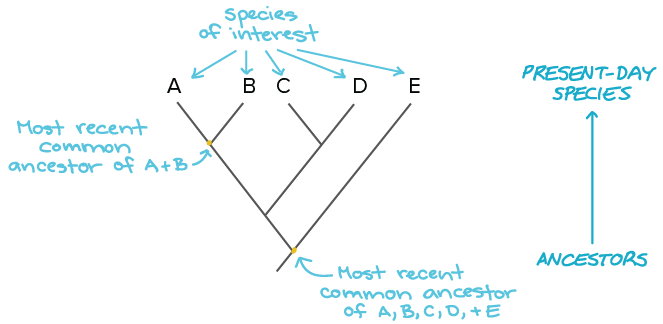
Building A Phylogenetic Tree Article Khan Academy

Nortemerida On Behance Design Visual Communication Editorial Design

With Your Flavors Combined Nerd Humor Science Humor Science Nerd

The Sphere Known As Netzach Meaning Victory On The Tree Of Life Tree Of Life Tree Of Life Art Yggdrasil Tree

Robert Sae Heng Sets The Record Straight Unicorns Have Beauty Narwhals Brains The Tiny Pencil Illustration Animal Illustration Plant Illustration

Loanword Music Genres Foreign Words Word Origins

Using Trees For Classification Understanding Evolution

Phylogeny Of Canid Species The Phylogenetic Tree Is Based On 15 Kb Of Download Scientific Diagram


Comments
Post a Comment